Make sure that your Ubuntu has already been updated before proceeding to the SQL configuration.
MySQL Installation
// Step 1
sudo apt install mysql-server
// Step 2
sudo mysqlOnce you entered MySQL, proceed with the Data Definition Language command (ALTER)
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH caching_sha2_password BY 'Password' //or anything you wantYou can proceed with exit command once you complete it.
Secure MySQL
This is for securing MySQL server deployment.
sudo mysql_secure_installationJust enter Y or y with all the available option until you find a prompt below:
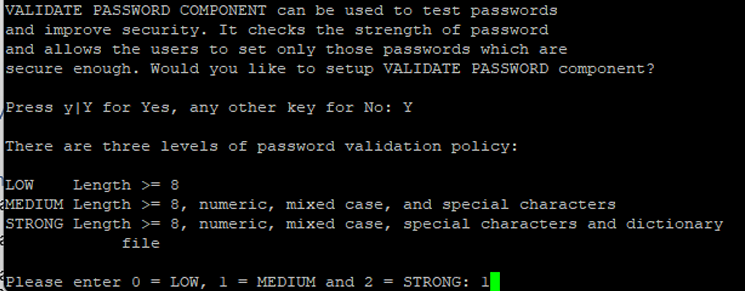
You can either use 1 (MEDIUM) or for high security 2 (STRONG). The levels will be indicating how strong and strict the password requirement is.
Proceed with the reference below:
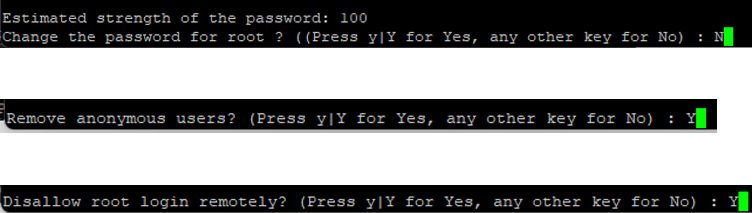
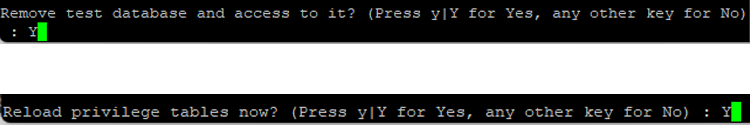
Setting MySQL Time
You can set the MySQL time with the following command. Access your MySQL and enter the command below:
mysql -u root -p
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE '%time_zone%';
SET GLOBAL time_zone = '+08:00';
exit Once that, follow the next command
sudo nano /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf //enter this on your terminal
//after you enter the text editor (nano) proceed with command below
[mysqld]
default-time-zone = '+08:00'
// to save this Ctrl + X and enter Y to save the changes
sudo systemctl restart mysql //execute system control restart in your Linux TerminalSetting SQL Mode
SQL modes for MySQL or MariaDB — it controls how the database handles invalid data, default values, and certain behaviors.
sudo nano /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf //execute this on terminal
// add this parameter in the text editor (nano)
[mysqld]
sql-mode =
"STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,
NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION"
// to save this Ctrl + X and enter Y to save the changes
sudo systemctl restart mysql //restart MySQL| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| STRICT_TRANS_TABLES | Enforces strict validation — if a column value is invalid (e.g., wrong type), MySQL rejects the insert/update instead of silently adjusting it. |
| NO_ZERO_IN_DATE | Disallows dates with zero month or day (e.g. 2024-00-15 or 2024-01-00). |
| NO_ZERO_DATE | Disallows the date '0000-00-00' — forces you to use a real date or NULL. |
| ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO | Raises an error if you divide by zero, instead of returning NULL or 0. |
| NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION | Prevents MySQL from silently using a different storage engine when the specified one is unavailable. |

Leave a Reply